Permeability
After reading this section you will be able to do the following:
- Describe what permeability is.
As previously mentioned, permeability (m) is a material property that describes the ease with which a magnetic flux is established in a component. It is the ratio of the flux density (B) created within a material to the magnetizing field (H) and is represented by the following equation:
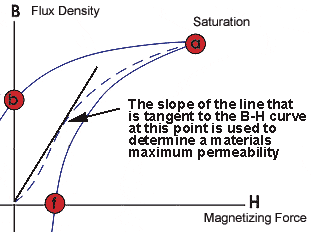
It is clear that this equation describes the slope of the curve at any point on the hysteresis loop. The permeability value given in papers and reference materials is usually the maximum permeability or the maximum relative permeability. The maximum permeability is the point where the slope of the B/H curve for the unmagnetized material is the greatest. This point is often taken as the point where a straight line from the origin is tangent to the B/H curve.
The relative permeability is arrived at by taking the ratio of the material's permeability to the permeability in free space (air).
Where:
The shape of the hysteresis loop tells a great deal about the material being magnetized. The hysteresis curves of two different materials are shown in the graph.
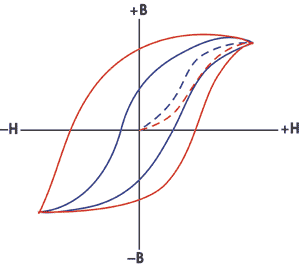
In magnetic particle testing, the level of residual magnetism is important. Residual magnetic fields are affected by the permeability, which can be related to the carbon content and alloying of the material. A component with high carbon content will have low permeability and will retain more magnetic flux than a material with low carbon content.
In the two B-H loops above, which one would indicative of a low carbon steel?
Answer:
- The material would exhibit high permeability because of its low carbon content.
- It would exhibit low reluctance or resistance to the magnetic field
- It would have low retentivity.
- The weak residual magnetism would require a low coercive force to remove it.
The B-H curve for a low carbon steel would, therefore, resemble the slender curve above.
Review:
- Permeability is a material property that describes the ease with which a magnetic flux is established in a component.
- The maximum permeability is the point where the slope of the B/H curve (hysteresis loop) for the unmagnetized material is the greatest.